- 04 Feb, 2026
- Artificial Intelligence
- Automation
- By Musketeers Tech
What Is AutoGPT? How It Works, Use Cases & Risks
If you’ve ever wished ChatGPT could take the wheel, plan a task, break it into steps, run those steps, and report back, then you’re already thinking in the direction of what is AutoGPT. In plain terms, AutoGPT is an open-source “agent” approach that aims to turn a single high-level goal (like “research competitors and draft a summary”) into a multi-step workflow executed with minimal back-and-forth prompting.
That autonomy is the upside, and also the reason people ask about cost, safety, and whether it’s actually better than ChatGPT for day-to-day business work. In this guide, we’ll cover how AutoGPT works, what it’s good at, where it can go wrong, and how to decide between AutoGPT and alternatives like AgentGPT or BabyAGI.
We’ll keep this practical for founders, product teams, and ops leaders, no hype, just the mechanics and the guardrails you need.
What is AutoGPT? (AutoGPT AI agents explained)
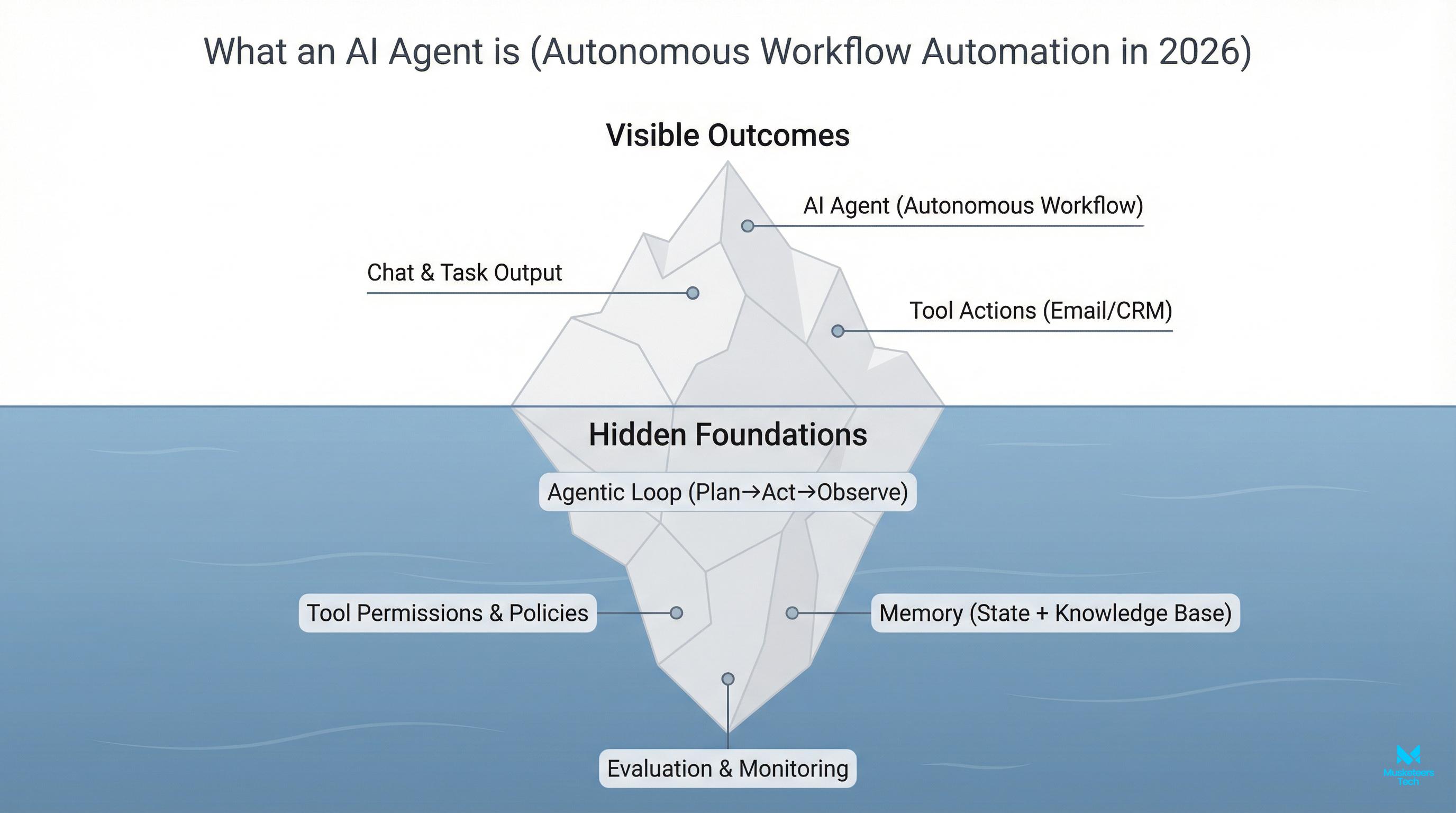
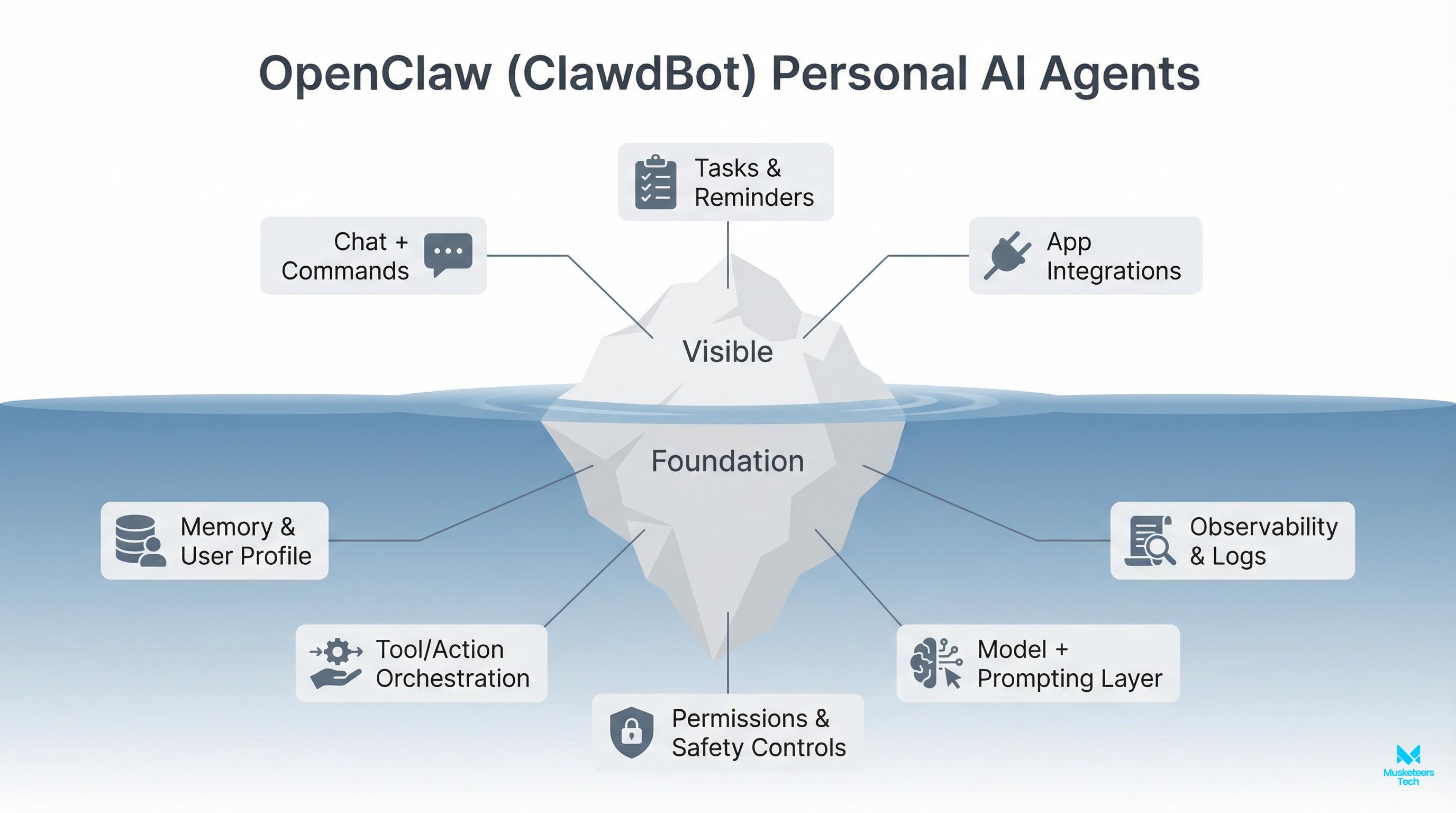
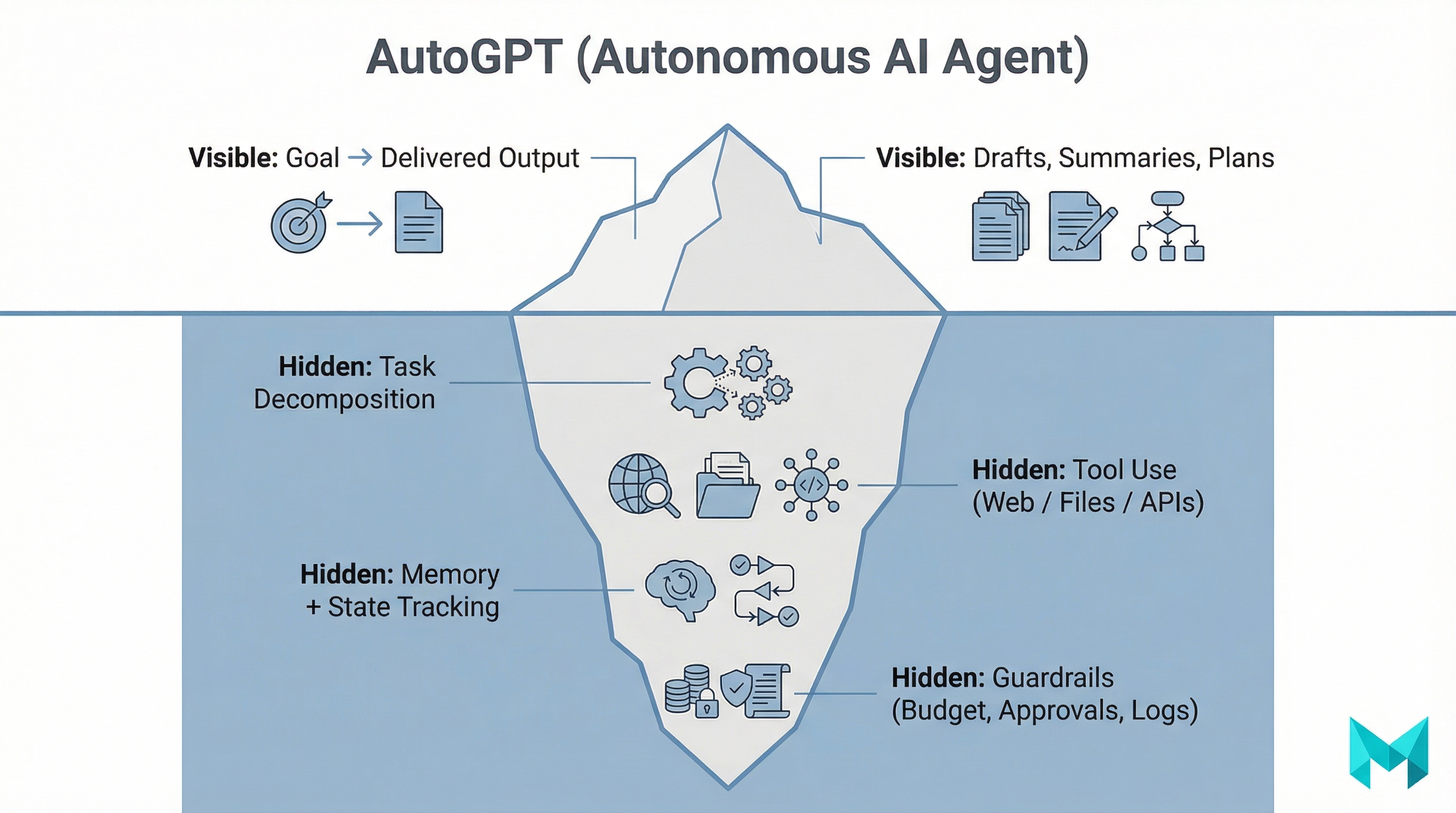
AutoGPT is commonly described as an open-source AI agent framework that can pursue a goal by generating and executing its own intermediate steps. Unlike a standard chat interface where a human must keep prompting, an agent-style system tries to:
- interpret your objective,
- create a task plan,
- execute tasks (often with tools like web browsing or file actions),
- evaluate progress,
- and iterate until it reaches a stopping condition.
Quick clarity
- AutoGPT isn’t a model. It uses an underlying large language model (LLM) via an API and wraps it in “agent” logic and tooling.
- “AutoGPT” is a spectrum now. The name can refer to the original GitHub project and to newer platform experiences. Always check which implementation you’re evaluating.
For reference, IBM’s explainer frames AutoGPT as a way to automate multi-step projects with AI agents, rather than relying on repeated prompts in a chat UI. Source: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/autogpt
If you’re already comparing approaches, you may also want our breakdown here: AutoGPT vs ChatGPT
Why AutoGPT matters: benefits for business workflows
AutoGPT became popular because it pointed toward a shift from “answering questions” to running workflows. When it works well, the benefits are very real:
- Less manual prompting: You define what you want, not every micro-step to get there.
- Repeatable processes: With the right structure, agents can turn one-off tasks into reusable flows (e.g., weekly competitor snapshots).
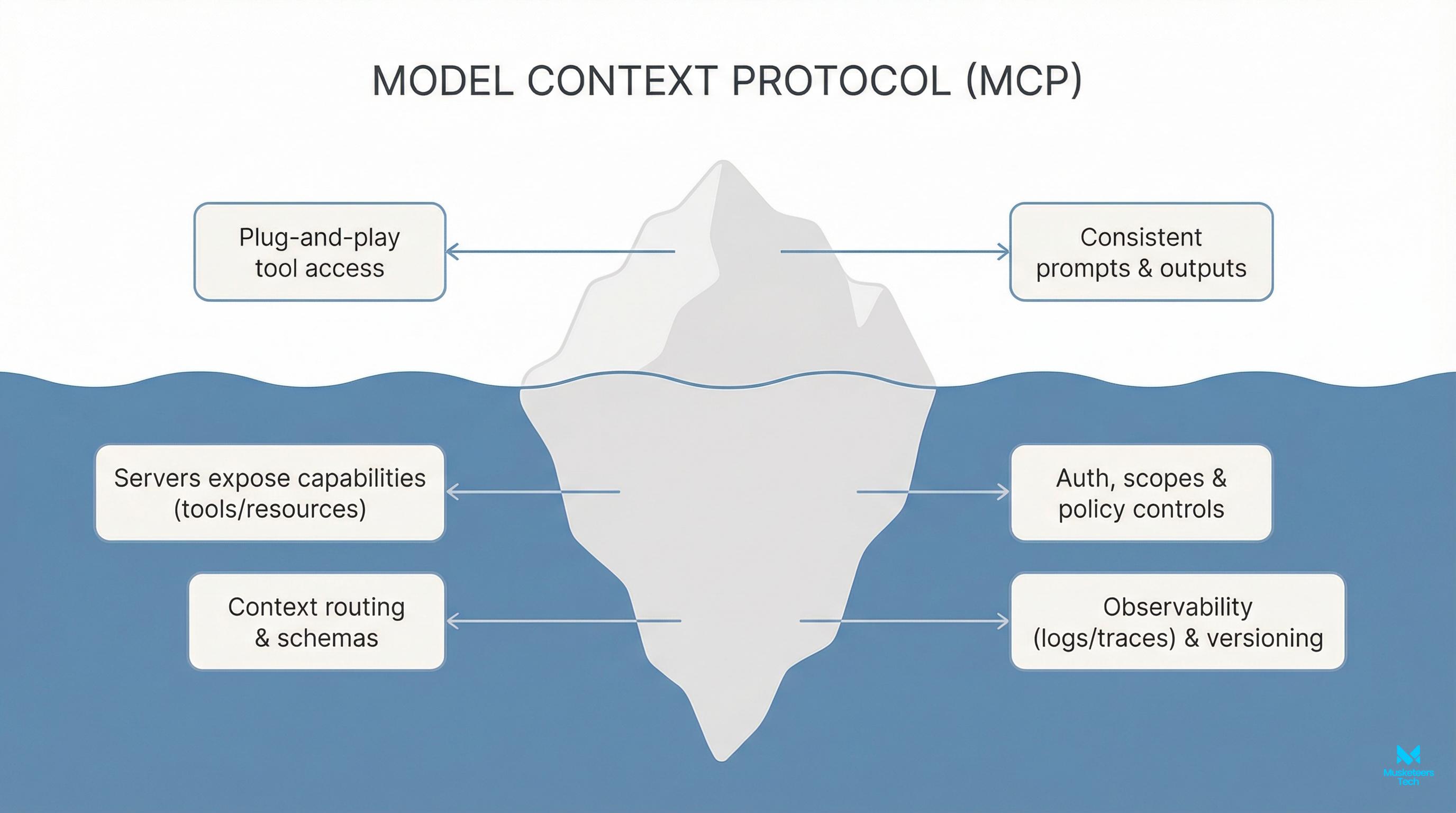
- Tool + data integration: Agent systems can connect to web search, internal docs, databases, and APIs so the output can reflect current information and your business context.
- Faster iteration loops: For tasks like summarizing research, drafting outlines, or organizing project notes, agentic loops can reduce context switching.
Where teams get value fastest is usually in semi-automated work: the agent produces a draft, and humans approve, edit, or run the final action.
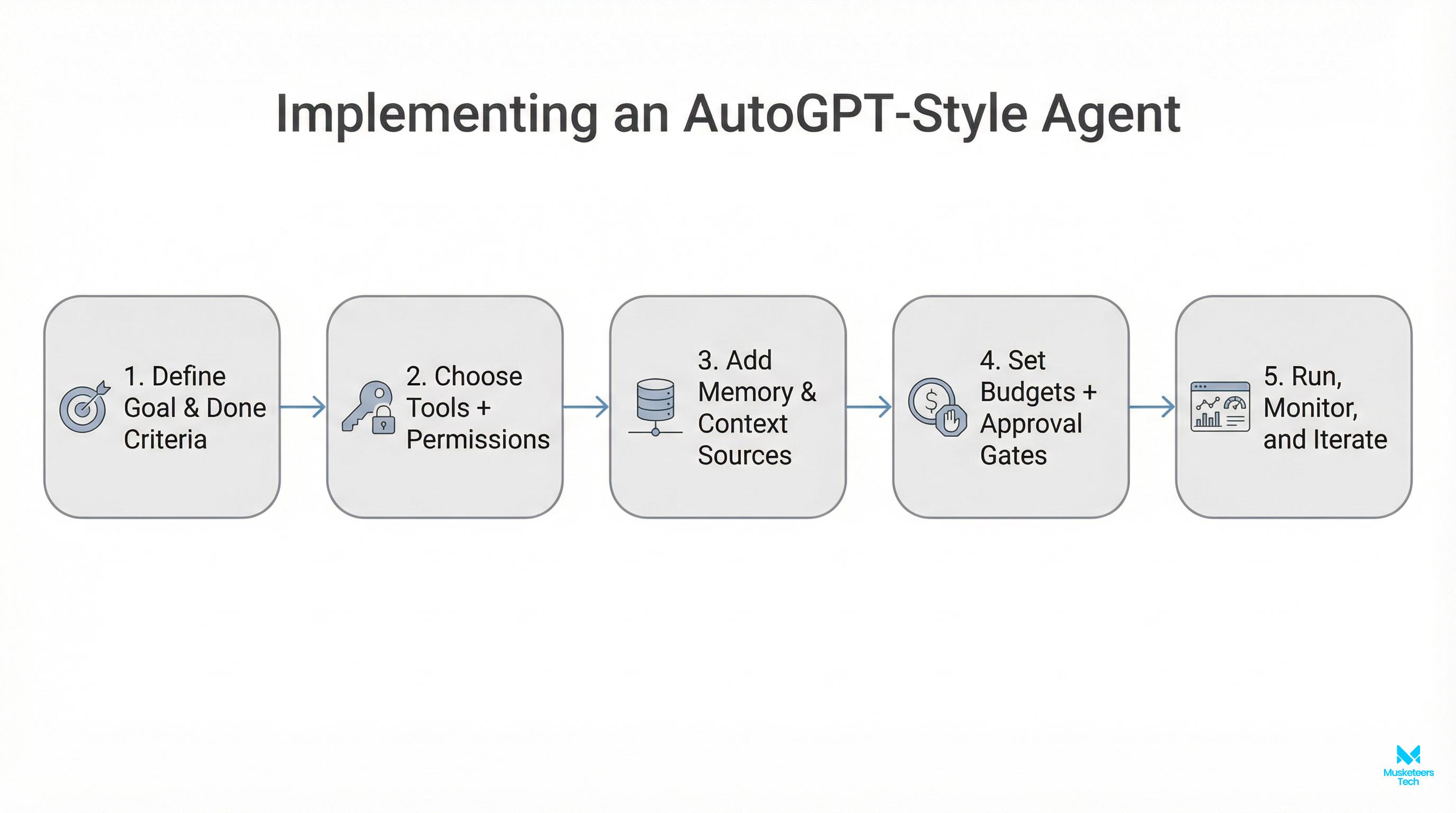
How does AutoGPT work? (agentic workflow, step-by-step)
Most AutoGPT-style systems follow a loop similar to this:
- Goal input: You provide a target outcome plus constraints (time, sources, tone, format, budget).
- Planning / task creation: The system decomposes the goal into smaller tasks (research, summarize, draft, validate).
- Task prioritization: It orders tasks so dependencies make sense (don’t draft before you collect sources).
- Execution with tools: The agent calls the LLM and (optionally) external tools like web browsing, code execution, file IO, API calls.
- Evaluation: It checks whether the output meets the goal; if not, it revises the plan and loops.
- Stop condition: It stops when it hits success criteria, a time/budget limit, or an error.
IBM describes this as user input -> task creation -> prioritization -> execution -> evaluation -> refinement -> completion (and notes it can fail, hallucinate, or get distracted). Source: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/autogpt
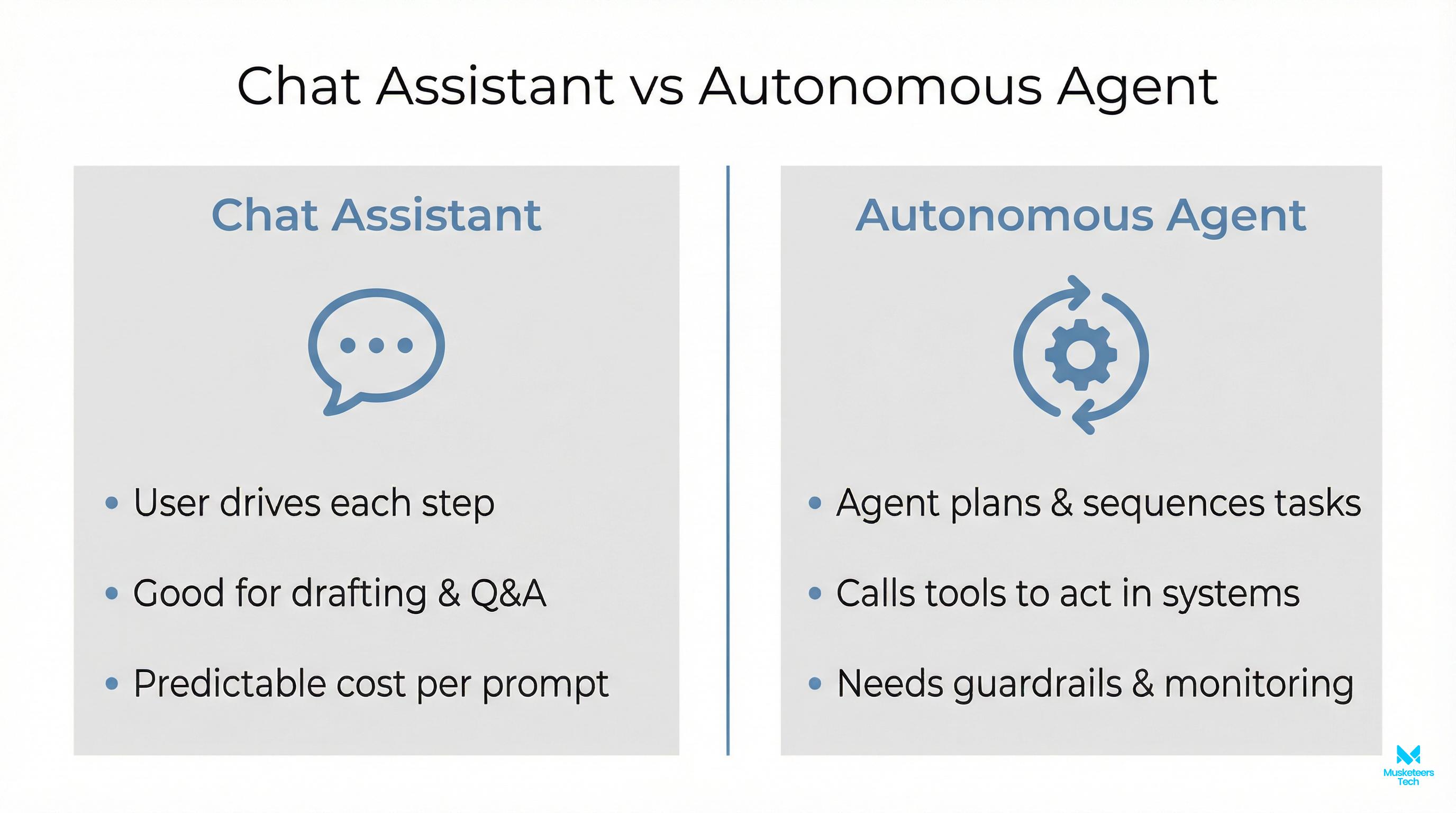
What makes this different from a chatbot?
A chatbot is mainly a single-turn or multi-turn conversation. An agent adds:
- state (what it has done),
- a plan (what it intends to do next),
- tool use (actions beyond generating text),
- and iteration (self-correction across steps).
That difference is why agent systems can feel powerful and why they also need controls.
Key features & differences (AutoGPT vs ChatGPT vs AgentGPT vs BabyAGI)
AutoGPT sits inside a broader ecosystem of “agentic AI.” Here’s a business-friendly comparison:
| Feature | AutoGPT (agent framework) | ChatGPT (chat assistant) | AgentGPT (browser agent UX) | BabyAGI (lightweight agent pattern) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary mode | Autonomously executes multi-step tasks | Conversational Q&A and drafting | Guided autonomy in-browser | Minimal agent loop + task list |
| Human involvement | Low-to-medium (should add approvals) | High (you drive steps) | Medium (you supervise) | Medium (DIY) |
| Tool integration | Often yes (varies by setup) | Limited by interface & plan | Typically limited/sandboxed | Depends on your build |
| Best for | Workflows, automation experiments, prototypes | Reliable writing, reasoning, planning | Quick demos, light research flows | Learning agent loops, simple automation |
| Risk profile | Higher if given file/web access | Lower (mostly text output) | Medium | Medium |
Practical takeaways:
- If you need reliability and tight control, ChatGPT-style assistants often win.
- If you need autonomy across steps, AutoGPT-style agents are more suitable but only with guardrails.
- If you want to test the concept quickly, AgentGPT-like experiences are often the fastest path.
- If you’re building an internal agent system, you’ll usually outgrow “one repo” and move toward an agent stack (orchestration, evaluation, observability, access control).
Use cases and practical AutoGPT examples
Here are realistic ways teams use AutoGPT-style agents especially when the workflow can be structured and checked.
1) Market and competitor research (repeatable briefs)
- Gather sources (news, competitor pages, pricing pages)
- Summarize changes since last run
- Produce a short “weekly brief” with citations
2) Sales enablement drafts (with approval gates)
- Draft account research notes
- Produce outreach variants per persona
- Create call prep sheets from public + internal notes
3) Support and ops knowledge workflows
- Triage a set of tickets
- Suggest response drafts + links to internal docs
- Escalate edge cases to humans
4) Product discovery support
- Cluster feedback themes from reviews
- Draft PRD sections or release notes
- Generate test cases from requirements
If your goal is to connect agentic workflows to proprietary data, this is the foundational skill: training an AI model on your own data
Best practices & common mistakes (safety-first guardrails)
Production tip
Autonomy without controls can lead to surprise bills, leaked secrets, or bad decisions. Put guardrails in place before granting broad tool access.
Best practices (do these first)
-
Start with narrow objectives
Good: Summarize 10 competitor feature pages and produce a 1-page comparison.
Risky: Build my entire go-to-market strategy. -
Add explicit constraints
Budget cap (tokens/$), time cap, allowed domains, allowed tools, required citations. -
Use a sandbox
Isolate the run (no production credentials, no write access to critical systems). -
Require human approval for irreversible actions
Sending emails, publishing content, changing records, deploying code. -
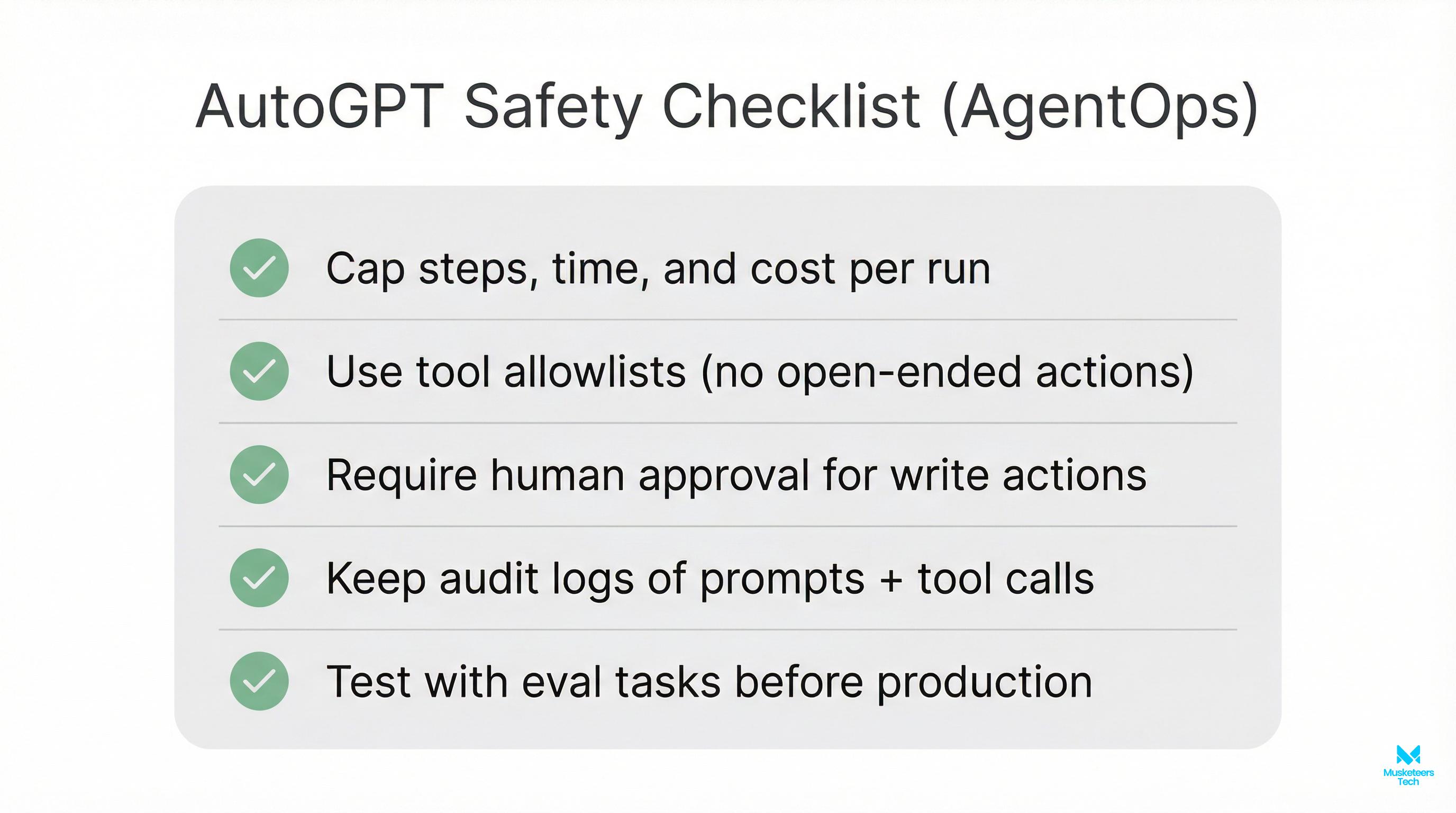
Log everything (AgentOps mindset)
Inputs, tool calls, outputs, costs, errors, and “why” traces for audits and debugging.
Common mistakes (and how to avoid them)
- Exposing API keys in repos or logs store secrets in a vault/secret manager; rotate keys.
- Letting the agent browse the whole web restrict to an allowlist and require citations.
- No evaluation step add a “critic” pass: check factuality, sources, and formatting before final output.
- Treating agent output as truth agents can hallucinate; always verify critical facts.
- Ignoring cost dynamics autonomous loops can multiply token usage quickly; enforce budgets.
A quick “business guardrails” checklist
- Budget limit (hard stop)
- Allowed tools + allowed domains
- Secrets management (never in prompts)
- Human-in-the-loop approvals
- Observability: logs + traces + cost reports
- Data policy: what can/can’t be sent to the LLM
Tools / platforms to explore (and where AutoGPT lives)
If you want to evaluate AutoGPT directly, start here:
- AutoGPT repository (GitHub): https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
- AutoGPT platform landing page: https://agpt.co/
- AgentGPT and BabyAGI (adjacent ecosystem keywords): useful for quick demos or learning loops
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
AutoGPT can be “better” for multi-step automation because it can plan and execute steps with less prompting. ChatGPT is often better for reliability, controlled interaction, and consistent writing where you want a human to direct each step. For deeper comparison, see: AutoGPT vs ChatGPT.
How Musketeers Tech Can Help
AutoGPT-style autonomy is exciting but most teams don’t need a demo agent. They need a reliable, secure, observable AI workflow that fits their product and data policies.
Musketeers Tech helps businesses design and build agentic systems with the guardrails that production environments require: scoped tools, approval gates, cost controls, and traceable logs for audits. If you want an AI agent to support sales, operations, or customer support, we can take you from a proof-of-concept to a deployable solution.
We’ve delivered AI-driven products and assistants—like our portfolio project: BidMate (an AI assistant for better bidding workflows)—and we can apply the same engineering discipline to your agent roadmap.
AI Agent Development
Design, build, and govern production-ready AI agents with sandboxing, approvals, and observability.
Generative AI Apps
Ship reliable GenAI workflows that connect to your data and tools—safely and at scale.
Final Thoughts
Now you have a practical answer to what is AutoGPT: it’s not just another chatbot, but an agent approach that can plan and execute multi-step work with less human prompting. That autonomy makes AutoGPT useful for repeatable workflows like research briefs, drafting support artifacts, and structured analysis but it also increases the need for guardrails like budgets, tool restrictions, approvals, and logging.
If you’re evaluating AutoGPT for your business, focus less on the hype and more on the workflow design: define success criteria, constrain the environment, and decide where humans must review outputs. Done right, agentic AI can reduce busywork and speed up teams without creating new risk.
Generative AI Application Services See Recent Projects