- 05 Feb, 2026
- Artificial Intelligence
- Product Strategy
- By Musketeers Tech
AutoGPT vs ChatGPT: What’s Different and When to Use Each
AutoGPT vs ChatGPT is a common comparison when teams move from “AI that answers to AI that does. Both are built on similar large language model (LLM) foundations, but they behave very differently in real workflows.
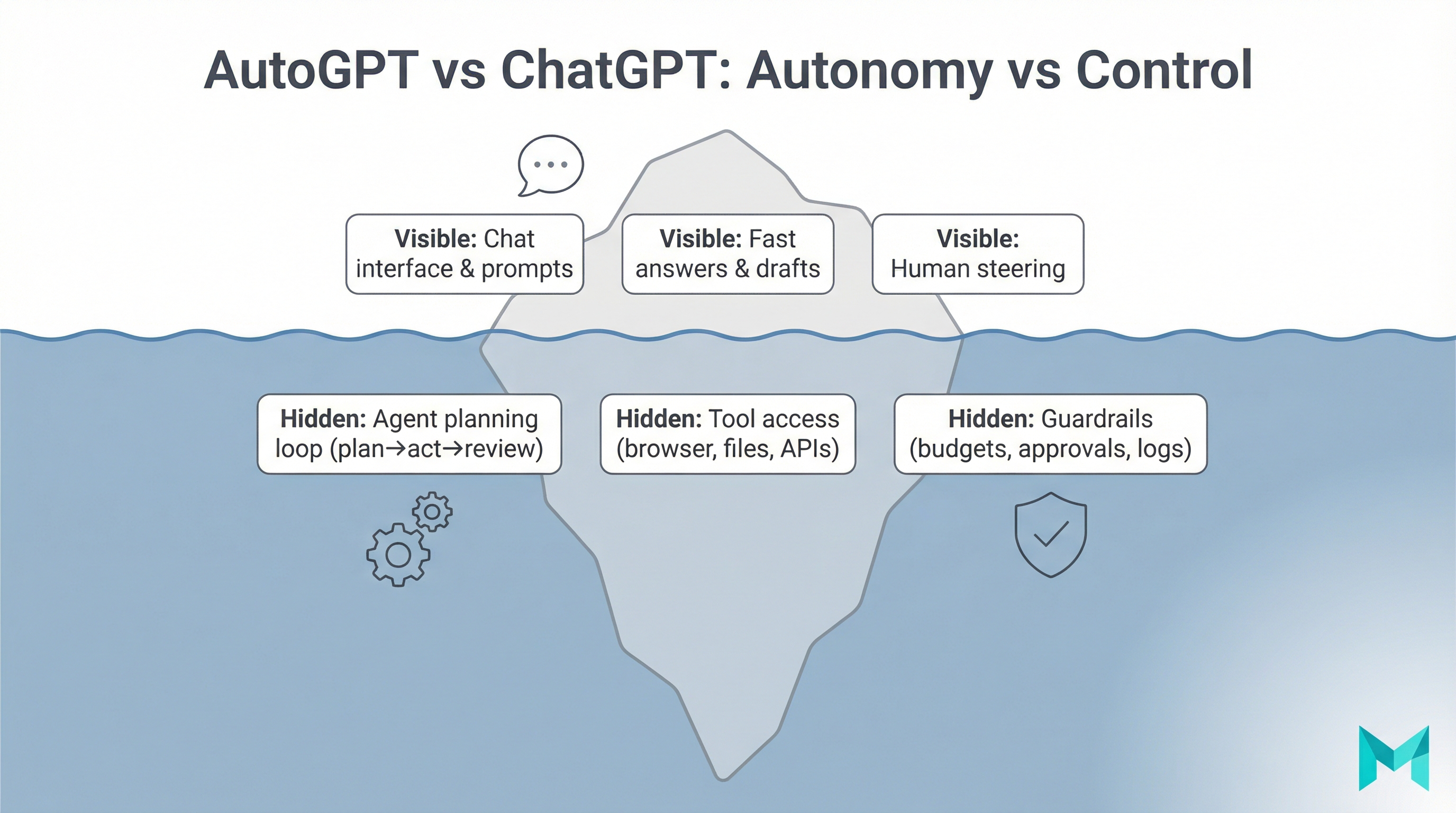
ChatGPT is usually best when you want interactive help: you ask, it answers, you refine. AutoGPT-style tools aim for autonomy: you give a goal, and the agent breaks it into steps, calls tools, writes files, and keeps going with limited supervision.
Founder takeaway: Do you need autonomy or control? This guide shows the differences, when to use each, and the guardrails you’ll want in place.

Quick Start
Skip to:
- Decision framework
- Safety checklist
- Real use cases
What is AutoGPT vs ChatGPT? (Quick definitions)
AutoGPT and ChatGPT often get grouped together, but they represent two different product patterns.
Auto-GPT is an autonomous agent concept: you provide an objective, and the system attempts to plan, execute, and iterate, often by chaining multiple LLM calls and using tools (browser/search, files, APIs, scripts). The original open-source project gained popularity in 2023 on GitHub and helped popularize agentic loops (plan -> act -> evaluate -> repeat). See the repo: https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
New to the concept? Read our guide on what Auto‑GPT is and how it works.
Mental Model
ChatGPT is a skilled teammate (you direct each step). AutoGPT-style agents are junior operators with initiative (they act toward a goal under guardrails).
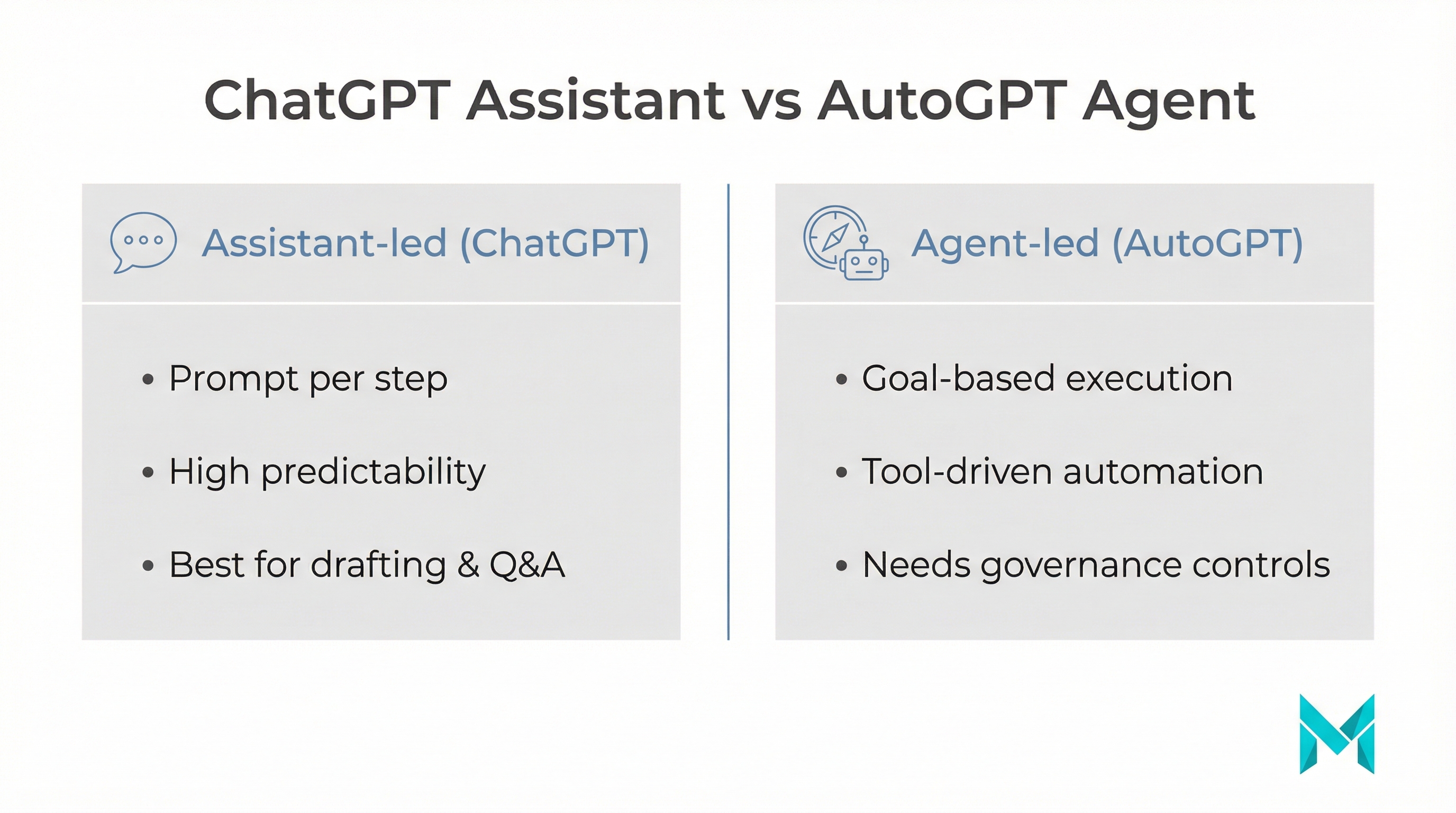
AutoGPT vs ChatGPT: Key differences (with a comparison table)
The biggest practical difference is autonomy and everything else (risk, cost, reliability) flows from that.
| Dimension | ChatGPT | AutoGPT-style agents |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction model | You prompt each step | You provide a goal; agent iterates |
| Best for | Drafting, Q&A, brainstorming, assisted coding | Multi-step workflows, research -> synthesize -> deliver |
| Control | High (human-in-the-loop) | Lower (needs policies, approvals) |
| Setup | Easy (web/app) | More setup (keys, tools, env) |
| Failure mode | Wrong answer you can catch | Wrong action or runaway loops if unguarded |
| Cost pattern | Predictable per session | Can spike due to long runs + tool calls |
Without guardrails, autonomy can turn mistakes into actions and drive up spend. Start narrow, add budgets and approvals, then expand.
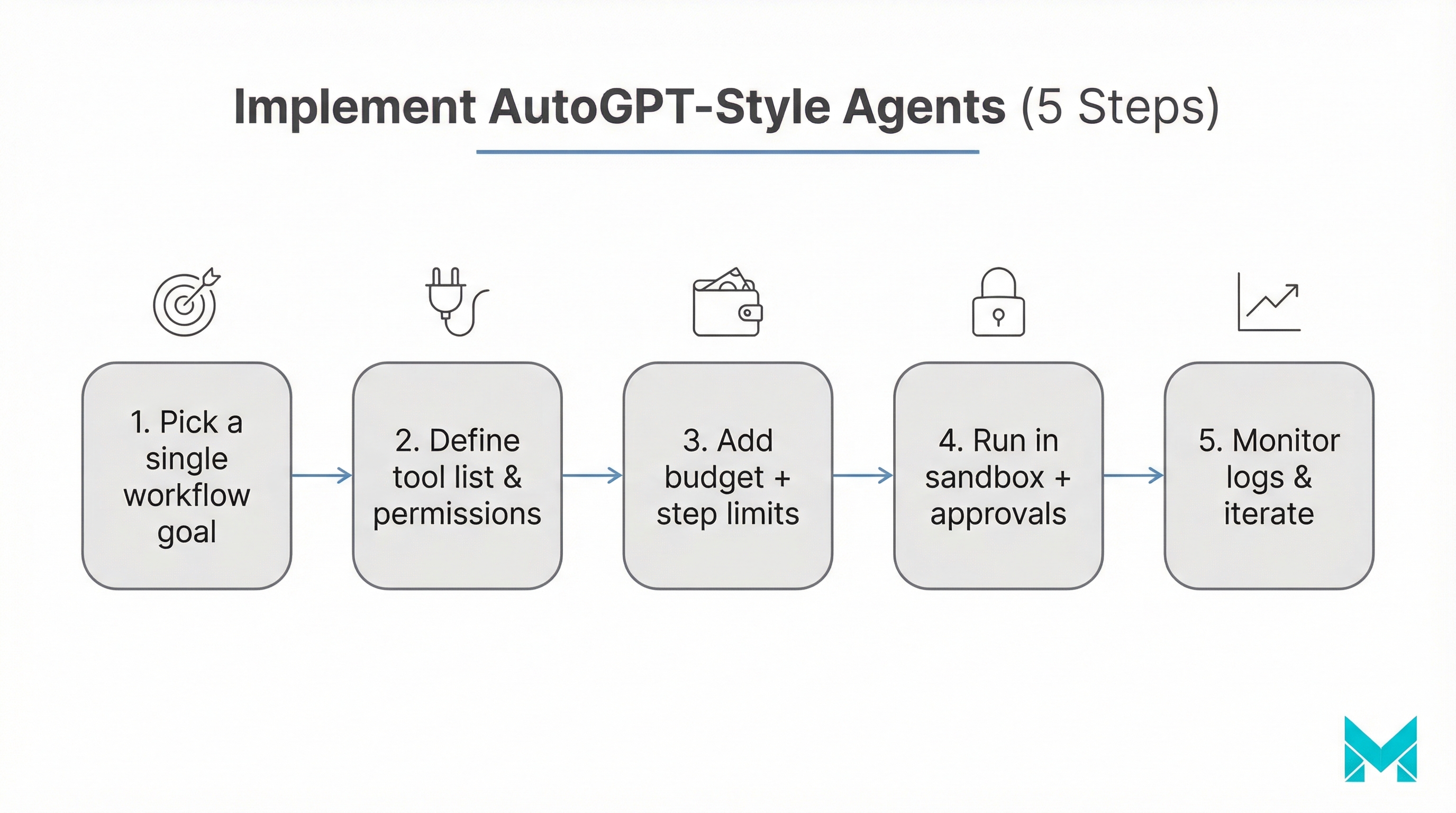
When to use Auto-GPT (practical use cases)
AutoGPT-style agents shine when the work is multi-step, repeatable, and tool-driven.
- Research -> synthesis -> deliverables: gather sources, extract key points, create a structured report, save it to files or a knowledge base.
- Monitoring and ops “watchdog”: crawl pages, flag issues, open tickets, draft fixes on a schedule.
- Content ops at scale: find outdated docs and propose updates still with editorial review.
- Back-office automations: reconcile data across tools (CRM, ERP, helpdesk) and produce daily summaries.
- Data enrichment: look up entities, verify records, and append structured fields with audit logs.
For product delivery inspiration, see these practical uses of AI in web development.
When to use ChatGPT (practical use cases)
ChatGPT is often the better first choice when correctness, tone, or strategy matter and when you want to talk it out.
- Drafting and refining (marketing, docs, emails): iterate quickly on landing pages, support macros, PRDs, user stories.
- Interactive problem-solving: discuss architecture tradeoffs, debug issues, generate and refine test cases.
- Human-in-the-loop workflows: legal, HR, medical, and brand voice decisions benefit from human judgment supported by ChatGPT’s drafts.
If your data is sensitive, consider retrieval over your private knowledge base rather than pasting raw context into prompts. Learn how to train ChatGPT on your own data safely.
Risks of AutoGPT-style autonomy (and the guardrails most teams miss)
Competitors mention “risks,” but founders usually need a concrete checklist. Here are the big ones to plan for.
The 5 biggest risks
- Runaway costs: agents can loop, call tools repeatedly, and rack up usage.
- Tool misuse: with browser, file, or terminal access, mistakes become actions.
- Data exposure: secrets in logs, prompts, files, or third-party tools.
- Hallucinated steps: the agent may sound confident and still be wrong.
- Unclear accountability: if no one owns monitoring, incidents get missed.
Agent Safety Checklist (practical guardrails)
- Permissioning: default to read-only; require approvals for write/delete/purchase actions.
- Sandboxing: run in isolated environments (containers, limited file systems).
- Secrets hygiene: use vaults/env vars; never hardcode keys into prompts or files.
- Budget caps: enforce max steps, tokens, tool calls, and timeouts.
- Observability: log decisions, tool calls, and outputs; keep replayable traces.
- Evaluation: spot-check outputs, run tests, and maintain “known good” baselines.
How to choose between AutoGPT vs ChatGPT (best practices + common mistakes)
Step-by-step decision framework
- Define the task shape: single-step/exploratory -> ChatGPT; multi-step with clear rules -> agent.
- Decide acceptable failure mode: wrong answer is okay -> agent viable; wrong action is unacceptable -> keep human-in-the-loop.
- List required tools: no tools needed -> ChatGPT; needs browser/files/APIs repeatedly -> agent.
- Set guardrails before you ship: approvals, budgets, logs, fallbacks.
- Pilot with a narrow scope: one workflow, one team, one success metric.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Giving too much access too early (terminal + production creds is risky).
- No cost controls (no step limit, no budget cap, no timeout).
- No evaluation plan (you can’t improve what you don’t measure).
- Trying to replace humans instead of augmenting them.

Tools & platforms to consider (beyond the labels)
- Auto-GPT (open-source): good for experimentation and learning the agent loop.
- AgentGPT: a lighter “agent in a browser” experience for demos/prototypes.
- LangChain (and similar): controlled tool-using agents built for production.
- Vector databases (e.g., Pinecone): memory/retrieval patterns in agent workflows.
- Monitoring + tracing: essential for debugging agent behavior over time.
If you want outcomes (not just experiments), treat agents like software: version them, test them, observe them, and roll them out gradually.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Not universally. AutoGPT-style agents are better when you need multi-step autonomy (research, monitoring, repeated workflows). ChatGPT is better when you need tight control, fast iteration, and human judgment at each step.
How Musketeers Tech Can Help
If you’re comparing AutoGPT vs ChatGPT because you want real business automation not just experiments Musketeers Tech can help you design the right agentic workflow with the right guardrails.
We build tool-using AI agents that fit your product and operating model: clear scopes, approval gates, budget controls, and audit logs so you can safely introduce autonomy. That typically includes retrieval over your knowledge base, integrations with CRMs/helpdesks, and evaluation to measure accuracy and ROI over time.
We’ve shipped GenAI experiences across domains, including projects like BidMate (an AI assistant that helps users win bids) and Chottay (AI order-taking for restaurants), where automation must be reliable and user-safe.
AI Agent Development
Design, build, and govern tool-using agents with approvals, budgets, and observability.
Generative AI Apps
From chat copilots to retrieval-augmented workflows—production-ready GenAI experiences.
Final Thoughts
AutoGPT vs ChatGPT isn’t a battle of “which AI is smarter.” It’s a choice between autonomy and control. If your workflow is conversational, creative, or judgment-heavy, ChatGPT is usually the safest, fastest path. If your workflow is repetitive, multi-step, and tool-driven and you’re ready to add budgets, approvals, and monitoring AutoGPT-style agents can unlock meaningful automation.
The best teams in 2026 don’t pick one forever. They build a system where ChatGPT helps humans think and communicate, while agents handle carefully-scoped execution behind guardrails.
Need help turning agent concepts into a production-ready workflow? Explore our AI agent development services or browse our recent projects.
Related Posts: