- 03 Feb, 2026
- Artificial Intelligence
- Customer Support
- By Musketeers Tech
AI Chatbot for Customer Service: A Practical 2026 Guide
Customer expectations for speed and availability keep rising—without giving support teams extra hours in the day. That’s why an ai chatbot for customer service has moved from a “nice-to-have” to a core part of modern support operations: it can answer repetitive questions instantly, route requests to the right place, and escalate complex issues to humans with context.
The catch
Many teams buy a tool, flip it on, and end up with frustrated customers stuck in dead-end loops—or a bot that confidently answers incorrectly. Treat your chatbot like a product: define what it should solve, connect it to the right data, add guardrails, and measure outcomes.
In this guide, you’ll learn what an AI customer service chatbot is, the four main chatbot types, real-world customer service chatbot examples, and a step-by-step setup plan you can use to launch safely. We’ll also cover how to choose the best platform based on ROI, integrations, and security.

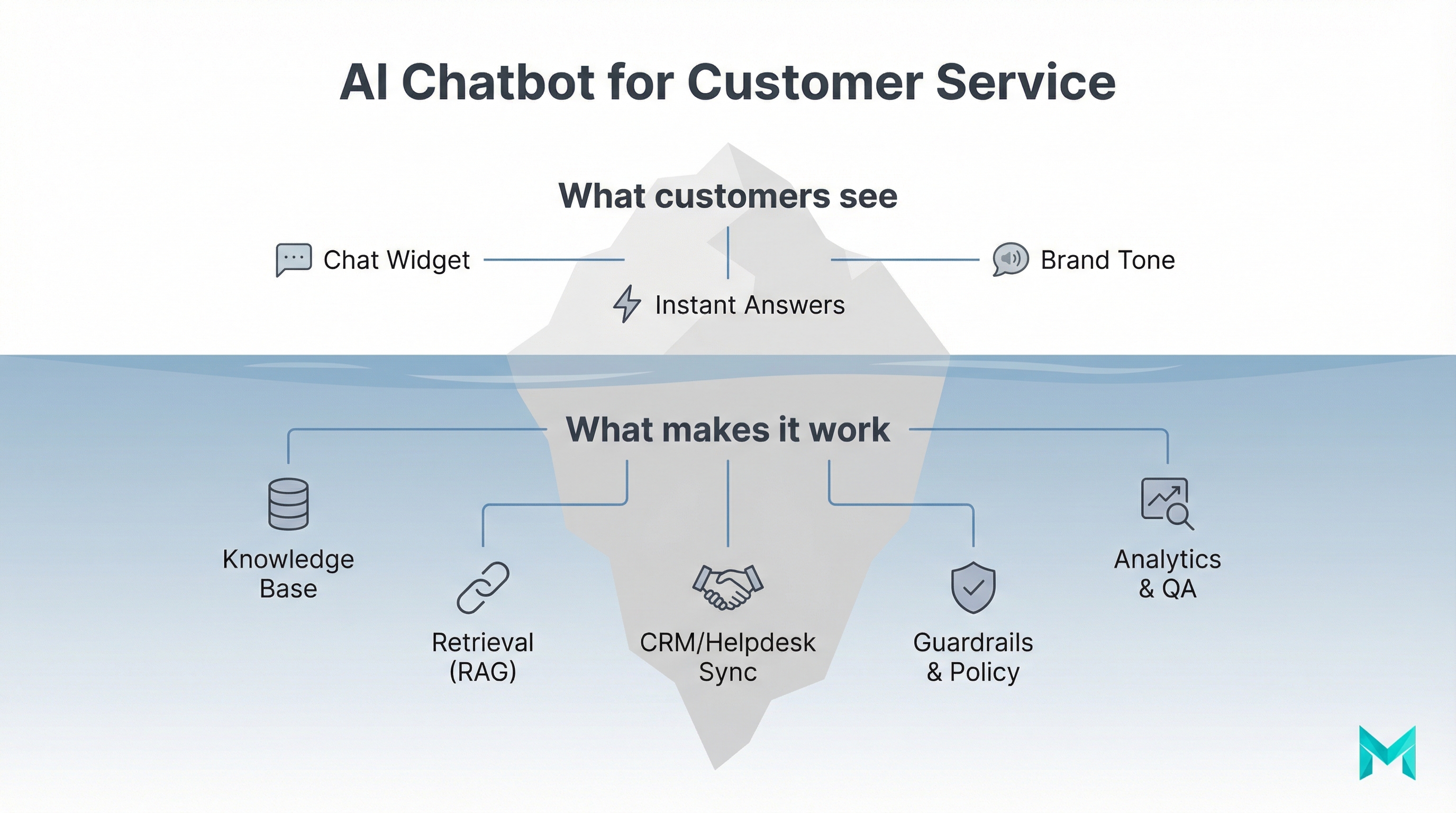
What is an AI chatbot for customer service? (AI powered chatbot for customer service)
An AI-powered chatbot for customer service is software that can communicate with customers in natural language (chat or voice) to answer questions, guide workflows (like returns), and hand off to a human agent when needed. Unlike basic “FAQ popups,†modern chatbots can:
- Understand intent (not just keywords)
- Pull answers from your knowledge base or product docs
- Personalize responses using customer/account context
- Trigger actions via integrations (e.g., create a ticket, update an order, schedule an appointment)
A useful way to think about it:
- Chatbots handle conversations.
- Automation handles actions (tickets, refunds, routing).
- AI improves understanding, personalization, and coverage—especially for messy, real-world language.
IBM’s overview frames chatbots as a scalable first line of support that reduces wait times and frees agents for nuanced cases, while also emphasizing that poor design can frustrate customers and damage trust (source: IBM Think, published 07 Nov 2025: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-customer-service-chatbots).
If you’re planning to connect a bot to your data (policies, help docs, account info), you may also want a “train on your own data” approach: training an AI model on your internal documentation
Why AI chatbots matter: benefits, costs, and measurable ROI
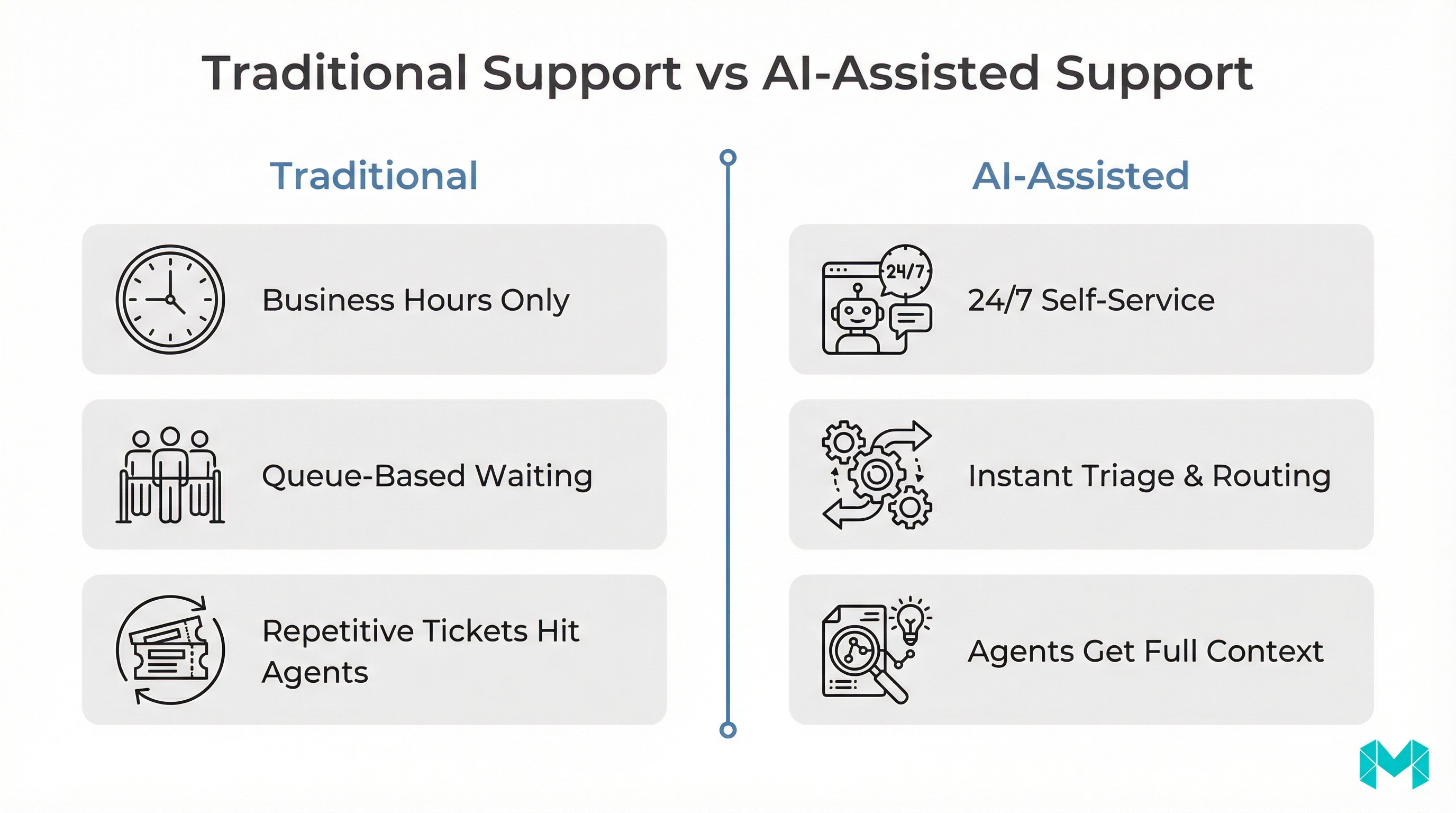
AI chatbots matter because they let you scale support without scaling headcount at the same rate—while improving response time. The most common business outcomes look like this:
- 24/7 coverage without staffing night shifts
- Faster first response time (FRT) and fewer “where is my order?” delays
- Consistent answers across website, in-app chat, and messaging channels
- Ticket deflection: fewer repetitive tickets make it to human agents
- Higher agent productivity: agents start with context instead of re-asking basics
- Better self-service: customers resolve issues without waiting in queue
- Better support reduces churn and improves renewals
- Bots can assist with lead qualification and product guidance (especially for B2B SaaS)
A credible directional benchmark from IBM’s roundup: Gartner predicted agentic AI could autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues by 2029, driving a 30% reduction in operational costs (IBM cites Gartner press release: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2025-03-05-gartner-predicts-agentic-ai-will-autonomously-resolve-80-percent-of-common-customer-service-issues-without-human-intervention-by-20290).
What to track (KPIs that prove value)
If you implement a chatbot and can’t measure impact, it will get turned off. Start with these:
- Containment rate: % conversations resolved by the bot without human handoff
- Deflection rate: % issues solved that otherwise would have become tickets
- CSAT after bot chat (and compare to human CSAT)
- Average handle time (AHT) for agents after bot triage
- Escalation quality: % escalations that include full context + correct routing
The four types of chatbots (and when each is the best fit)
The “best” chatbot depends on your support maturity, risk tolerance, and integrations. Here are the four types of chatbots most teams encounter:
| Chatbot type | Best for | Strengths | Limitations | Typical data source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based (decision tree) | Simple FAQs, fixed flows | Predictable, safe, easy to audit | Breaks on unfamiliar phrasing | Prewritten scripts |
| NLP intent bot | Known intents (shipping, billing, password reset) | Better understanding than rules, scalable | Needs ongoing intent training | Intent library + KB |
| LLM chatbot (generative) | Broad Q&A over lots of docs | Handles natural language well | Can hallucinate without guardrails | Docs + KB (often with retrieval) |
| Agentic AI (tool-using) | End-to-end resolutions (refunds, updates) | Can take actions across systems | Highest governance/security burden | APIs + CRM/helpdesk + policies |
How to pick quickly (a simple heuristic)
- If you need maximum control and have a small FAQ set → start rule-based.
- If you have repeatable categories of issues and want scale → NLP intent bot.
- If you have a large knowledge base and varied customer wording → LLM + retrieval.
- If you want the bot to do the work (not just answer) → agentic AI + integrations.
Most modern deployments are hybrid: an LLM for language + retrieval for accuracy + deterministic workflows for sensitive steps (billing, account changes).
Customer service chatbot examples (use cases by team)
If you’re wondering what “good” looks like in practice, these are common, high-ROI patterns.
1) Ecommerce & DTC
- Order status / shipping updates
- Returns and exchanges eligibility
- Product recommendations and sizing help
- Cart abandonment prompts (careful: don’t be spammy)
2) B2B SaaS support
- “How do I…?” product guidance from docs
- Troubleshooting known errors
- Account/billing routing (handoff to humans for changes)
- Ticket triage: categorize, collect logs, link relevant KB articles
3) Services businesses (clinics, agencies, local services)
- Appointment scheduling and rescheduling
- Pre-qualification questions
- Policy answers (cancellations, pricing ranges)
- Follow-ups and reminders
4) Internal support (IT/HR)
- Password resets and tool access steps
- Policy Q&A
- Request intake with structured fields
Pro tip
Start with the top 10–20 ticket drivers and design flows for those first. That’s where containment and deflection come fastest.
How to set up an AI chatbot for customer service (step-by-step rollout)
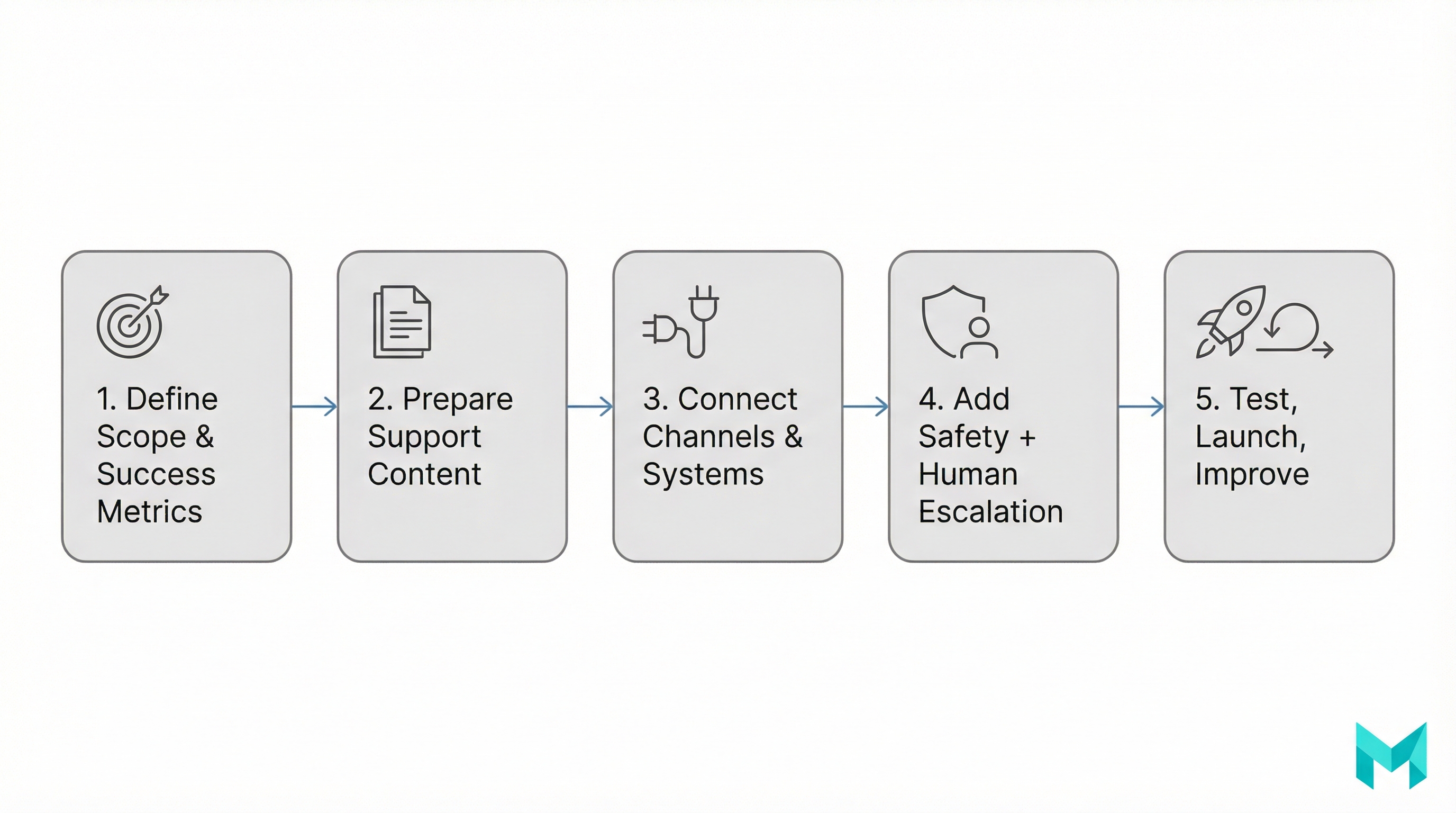
A safe setup process is less about “turning on AI” and more about building a reliable support system. Here’s a proven rollout you can run in 2–6 weeks, depending on integrations.
Step 1: Define scope (and what the bot must not do)
Write down:
- Top intents the bot should cover (e.g., “reset password,” “cancel subscription,” “refund policy”)
- “Red lines” (medical advice, legal promises, high-risk billing actions)
- Required escalation triggers (angry sentiment, repeated failure, VIP accounts)
Step 2: Prepare your knowledge base (your bot is only as good as your docs)
Minimum sources:
- Help center articles
- Pricing and policy pages
- Product documentation / SOPs
- Common macros used by agents
If your documentation is messy, fix it first. Retrieval systems amplify quality—good or bad.
Step 3: Choose an answer strategy (RAG beats “just ask the model”)
For most businesses, the safest approach is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation):
- User asks a question
- System retrieves relevant passages from approved sources
- LLM answers using those passages (and cites internally)
This reduces hallucinations and makes updates easier (change docs → bot improves without retraining).
Step 4: Integrate with your helpdesk + CRM
If you want the bot to actually reduce workload, it needs to:
- Create/update tickets with conversation context
- Detect existing customers (account lookup)
- Route by category, priority, language, and sentiment
Common integrations: Zendesk, Intercom, Freshdesk, Salesforce, HubSpot.
If you’re building this into your site/app: web application development services
Step 5: Design the human handoff (avoid “trap loops”)
Your handoff should:
- Offer a clear “Talk to a human” path
- Transfer transcript + detected intent + collected fields
- Set expectations (An agent will reply in ~2 hours)
This single feature often determines whether customers love or hate the bot.
Step 6: Add guardrails and compliance basics
At minimum:
- Don’t ask for sensitive data in chat (or mask it)
- Log consent where required
- Define retention policies for transcripts
- Enforce “allowed tools/actions” for agentic workflows
- Add a fallback response: “I’m not sure” let me connect you.
Step 7: Test with real transcripts, then launch gradually
Use:
- Historical tickets as evaluation prompts
- A staging environment with internal users first
- A limited launch (off-hours or a subset of users/pages)
Step 8: Monitor, measure, and iterate weekly
Review:
- Top failure intents
- Escalation reasons
- CSAT deltas
- Hallucination reports (and which sources caused them)
A chatbot is not “set and forget.” It’s continuous improvement.
Best practices & common mistakes (2026 reality check)
Best practices that consistently work
- Start narrow, then expand: prove ROI on top issues first.
- Keep tone consistent across website, in-app, and social channels.
- Use sentiment + priority to escalate faster when risk is high.
- Make answers verifiable: use retrieval and internal citation.
- Treat it like a product: backlog, releases, and QA.
Common mistakes that kill trust
Avoid these pitfalls
- Launching without a knowledge base cleanup
- No clear human handoff (customers feel trapped)
- Allowing the bot to “guess” about billing/legal policies
- Measuring only “number of chats” instead of containment/CSAT
- Forgetting multilingual needs until after complaints start
Where the “10–20–70 rule” fits
Some teams use a “10–20–70” framing to plan effort:
- 10% model/tool choice
- 20% initial setup (intents, flows, integrations)
- 70% ongoing work (content upkeep, evaluation, monitoring, improvements)
Whether you follow this exact split or not, the point holds: long-term success is mostly operations and iteration—not picking a vendor.
Tools & platforms: how to choose the best AI chatbot for customer service
People searching “best ai chatbot for customer service” are usually deciding between buying a platform and building a custom assistant.

Buy a platform when
- You need fast time-to-value (days/weeks)
- Your use cases are standard (FAQ, ticket triage, basic workflows)
- You’re comfortable with vendor constraints
- You want built-in analytics and support features
Build (or customize deeply) when
- You need unique workflows (industry compliance, complex routing, specialized data)
- You need tight control over data, logging, and governance
- You want a differentiating support experience (not a generic bot)
- You’re moving toward agentic automation across systems
A practical evaluation checklist
Before you commit, ask:
- Can it integrate with our helpdesk and CRM cleanly?
- Does it support RAG over our approved sources?
- What security standards are supported (SOC 2, GDPR alignment)?
- Can we control tone, refusal behavior, and escalation rules?
- How are conversations evaluated (quality + safety)?
- What is pricing based on (seats, resolutions, conversations)?
If you want an implementation-first path (not just a vendor list), that’s exactly what our team builds: AI agent development
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The best AI chatbot is the one that matches your channels (web, in-app, WhatsApp), integrates with your helpdesk/CRM, and achieves high containment without harming CSAT. For most teams, “best” means strong knowledge-base retrieval (RAG), reliable handoff to humans, and clear analytics for ROI.
How Musketeers Tech Can Help
At Musketeers Tech, we help teams deploy AI chatbots for customer service that are actually reliable in production—meaning they’re connected to the right data, designed with safe escalation, and measured with clear ROI.
If you want a chatbot that goes beyond “answering FAQs,” we can build an AI support assistant that integrates with your helpdesk and CRM, uses retrieval (RAG) to reduce hallucinations, and follows governance rules (logging, privacy, role-based actions). For teams aiming for automation, we also develop agentic workflows that can complete multi-step tasks through approved APIs.
AI Agent Development
Design and deploy production-grade chatbots and agentic workflows with guardrails and analytics.
Generative AI Apps
RAG over your knowledge base, evaluations, and monitoring for safer AI in support.
Relevant experience includes building conversational and AI-driven products such as:
Learn more about our AI Agent Development and Generative AI Application Services, or see how we helped clients with similar challenges in our portfolio.
Talk to an Expert View PortfolioFinal Thoughts
An AI chatbot for customer service can be one of the fastest ways to improve response times and reduce repetitive tickets—but only if you implement it with the right foundations: clear scope, clean knowledge sources, retrieval-based answering, safe human handoff, and ongoing measurement.
If you’re early, start with the top ticket drivers and launch gradually. If you’re scaling, focus on integrations and governance so your bot can personalize responses and take approved actions without creating risk. And if you’re evaluating vendors, don’t stop at feature lists—run a real transcript-based test and compare containment, CSAT, and escalation quality.
Need help building or upgrading an AI chatbot for customer service? Check out our AI agent development services or explore our recent projects.
Related Posts: